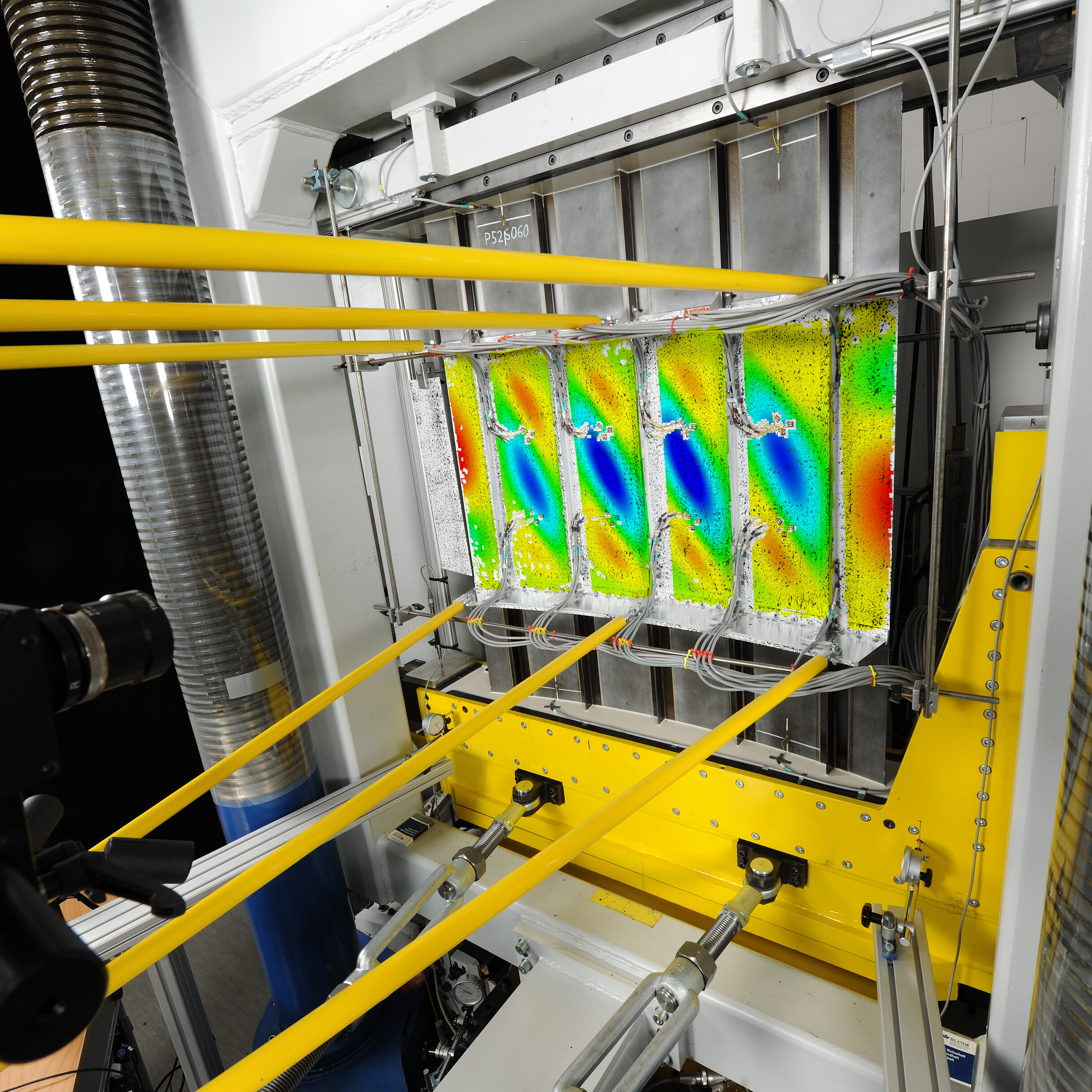
Making sustainability tangible – from a linear to a circular economy
The Department of Sustainability Technologies aims to develop the full sustainability potential of lightweight system construction. In its efforts to do this, it seeks to close gaps in expertise, capabilities and technologies for sustainability assessment and circular technologies in industry and research.
Expertise
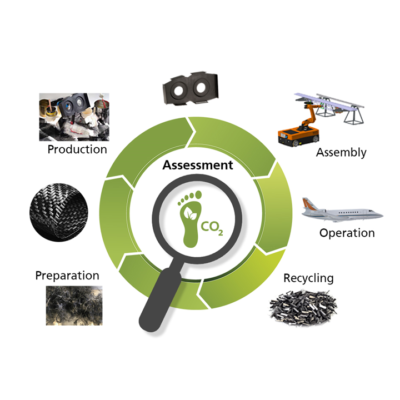
With its research in the field of sustainability assessment, the department creates the necessary conditions for the targeted development and improvement of sustainable solutions. Lightweight systems technologies are an important building block for achieving minimal emissions in future, but quantifiable evaluation of their potential represents a major challenge due to the complex interaction between different disciplines. Transparent, comprehensible and quantitative assessment of sustainability is carried out through careful and standardised modelling, the conscientious use of internal and external data sources and the application of appropriate and adapted metrics. This provides the basis for improving the environmental footprint and eco-efficiency of lightweight system construction in a targeted manner.
In its research into circular technologies, the department is developing separation and dismantling technologies alongside processes for recycling and reprocessing fibre composites. Research in these areas offers a variety of options for transitioning from a linear approach to a value-preserving circular economy, whereby sustainability can be evaluated and thus made tangible.
Service profile
- Sustainability assessment for lightweight systems
- Generation and provision of universally usable data and models for life cycle assessment and cost evaluation
- Development and provision of customized tools for environmental and economic evaluation
- Transparent assessment of the environmental impact and costs of technologies and processes in a circular economy
- Identification of areas of action for increasing sustainability
- Development of circular technologies that preserve value
- Dismantling technologies to reuse components
- Separation processes for sorted material flows
- Adapted recycling processes
- Processing of recycled materials